Blog
Understanding Tonsillitis: Symptoms, Causes, and Risks
Introduction
Tonsillitis, a prevalent condition, occurs when the tonsils, the soft tissue lumps at the back of the throat, become infected. This article aims to shed light on tonsillitis symptoms, causes, and potential complications.
What is Tonsillitis?
Definition
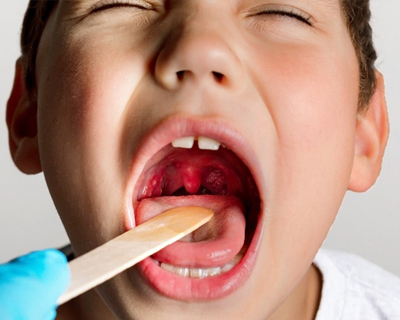
Tonsillitis is an infection affecting the tonsils, integral components of the immune system. These two small soft tissue lumps, located on either side of the throat, can be visualized by opening the mouth and sticking out the tongue.
Immune System Role
- Tonsils act as germ traps, aiding in preventing illnesses.
- Infection leads to swelling, soreness, and discomfort during swallowing, commonly referred to as a sore throat.
Symptoms and Causes
Tonsillitis Symptoms
-
Sore or Scratchy Throat:
- Often the initial sign. A sore or scratchy throat can be a sign of a cold or the flu. It can also cause inflammation of the tonsils and adenoids, which can lead to an ear infection.
-
Pain or Difficulty Swallowing:
- Swollen tonsils can impede the swallowing process. This may cause pain or discomfort when eating or drinking. In some cases, it can cause coughing, gagging, or even vomiting.
-
Red, Swollen Tonsils and Throat:
- The inflammation is visible to the naked eye. Having trouble swallowing is a common symptom of this condition. It can be caused by a virus or bacteria, and may require antibiotics.
-
White Spots on Tonsils:
- An infection is indicated by the appearance of these symptoms. These white spots are caused by the accumulation of white blood cells in the tonsils. This is a sign of an infection and should be checked by a doctor. Treatment may be necessary to clear the infection.
-
Coating on Tonsils:
- White, yellow, or gray coating may be present. This coating is a sign of inflammation of the tonsils and can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Treatment options include antibiotics or home remedies such as gargling with salt water or sucking on throat lozenges.
-
Fever:
- Temperature above 100.4°F (38°C).
-
Swollen Lymph Nodes:
- Glands on the neck sides may grow. Swollen lymph nodes are often a sign of an infection or irritation in the body. After a few weeks, they usually disappear on their own. However, if they persist, it is important to see a doctor.
-
Stomachache or Vomiting:
- More common in younger children. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including indigestion, food poisoning, and viral infections. Treatment typically includes rest and fluids, as well as medications to reduce discomfort.
First Signs of Tonsillitis
-
Sudden Sore Throat:
- Keep an eye on tonsils for redness or swelling. If the sore throat is accompanied by a fever, rash, or difficulty breathing, seek immediate medical help. Gargle with warm salt water to loosen secretions and help relieve the pain. Drink plenty of fluids, and take over-the-counter pain relievers as necessary.
Tonsillitis Causes
Viral Tonsillitis
-
Common Cold and Flu:
- Up to 70% of the cases are attributed to this group.
- Generally milder symptoms than bacterial tonsillitis.
Bacterial Tonsillitis (Strep Throat)
-
Group A Streptococcus:
- Commonly known as strep throat.
- Causes more severe symptoms than viral tonsillitis.
How Tonsillitis Spreads
-
Highly Contagious:
- Spread through kissing, sharing utensils, close contact, touching contaminated surfaces, and inhaling airborne particles from sneezing or coughing.
Risk Factors
-
Age Between 5 and 15:
- Most common in children and adolescents. This age group is also more prone to anxiety and depression. It is important to provide adequate support to this age group to help them manage their emotions. Early intervention is essential to reduce the risk of developing more serious mental health issues in the future.
-
Frequent Exposure to Germs:
- Higher risk for those in crowded environments like schools or workplaces. Washing hands regularly and avoiding touching your eyes, nose, and mouth can help to reduce the spread of germs. Wearing a mask in public can also help to protect oneself from germs.
Complications of Tonsillitis
-
Obstructive Sleep Apnea:
- Disrupted sleep breathing.
-
Peritonsillar Abscess:
- Collection of pus around the tonsils.
-
Tonsil Stones:
- Formation of hardened masses in tonsil crevices.
-
Tonsillar Cellulitis:
- Infection of the tonsils and surrounding tissues.
Complications Associated with Untreated Bacterial Tonsillitis
-
Poststreptococcal Reactive Arthritis:
- Joint pain and swelling caused by Strep infection.
-
Rheumatic Fever:
- Inflammatory disorders affect the heart, joints, and skin.
-
Scarlet Fever:
- Rash and fever are caused by streptococcal bacteria.
-
Kidney Inflammation:
- Inflammation of the kidneys.
Conclusion
Understanding tonsillitis, its symptoms, and associated complications is crucial for timely identification and management. If you or someone you know experiences persistent symptoms, consulting a healthcare professional is essential to ensure proper treatment and reduce the risk of potential complications.